





Fast and lightweight x86/x86-64 disassembler library.
## Features
- Supports all x86 and x86-64 (AMD64) instructions and [extensions](./include/Zydis/Generated/EnumISAExt.h)
- Optimized for high performance
- No dynamic memory allocation ("malloc")
- Thread-safe by design
- Very small file-size overhead compared to other common disassembler libraries
- [Complete doxygen documentation](https://zydis.re/doc/3/)
- Absolutely no third party dependencies — not even libc
- Should compile on any platform with a working C99 compiler
- Tested on Windows, macOS, FreeBSD, Linux and UEFI, both user and kernel mode
## Quick Example
The following example program uses Zydis to disassemble a given memory buffer and prints the output to the console ([more examples here](./examples/)).
```C
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{
ZyanU8 data[] =
{
0x51, 0x8D, 0x45, 0xFF, 0x50, 0xFF, 0x75, 0x0C, 0xFF, 0x75,
0x08, 0xFF, 0x15, 0xA0, 0xA5, 0x48, 0x76, 0x85, 0xC0, 0x0F,
0x88, 0xFC, 0xDA, 0x02, 0x00
};
// Initialize decoder context
ZydisDecoder decoder;
ZydisDecoderInit(&decoder, ZYDIS_MACHINE_MODE_LONG_64, ZYDIS_ADDRESS_WIDTH_64);
// Initialize formatter. Only required when you actually plan to do instruction
// formatting ("disassembling"), like we do here
ZydisFormatter formatter;
ZydisFormatterInit(&formatter, ZYDIS_FORMATTER_STYLE_INTEL);
// Loop over the instructions in our buffer.
// The runtime-address (instruction pointer) is chosen arbitrary here in order to better
// visualize relative addressing
ZyanU64 runtime_address = 0x007FFFFFFF400000;
ZyanUSize offset = 0;
const ZyanUSize length = sizeof(data);
ZydisDecodedInstruction instruction;
while (ZYAN_SUCCESS(ZydisDecoderDecodeBuffer(&decoder, data + offset, length - offset,
&instruction)))
{
// Print current instruction pointer.
printf("%016" PRIX64 " ", runtime_address);
// Format & print the binary instruction structure to human readable format
char buffer[256];
ZydisFormatterFormatInstruction(&formatter, &instruction, buffer, sizeof(buffer),
runtime_address);
puts(buffer);
offset += instruction.length;
runtime_address += instruction.length;
}
}
```
## Sample Output
The above example program generates the following output:
```asm
007FFFFFFF400000 push rcx
007FFFFFFF400001 lea eax, [rbp-0x01]
007FFFFFFF400004 push rax
007FFFFFFF400005 push qword ptr [rbp+0x0C]
007FFFFFFF400008 push qword ptr [rbp+0x08]
007FFFFFFF40000B call [0x008000007588A5B1]
007FFFFFFF400011 test eax, eax
007FFFFFFF400013 js 0x007FFFFFFF42DB15
```
## Build
#### Unix
Zydis builds cleanly on most platforms without any external dependencies. You can use CMake to generate project files for your favorite C99 compiler.
```bash
git clone --recursive 'https://github.com/zyantific/zydis.git'
cd zydis
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
```
#### Windows
Either use the [Visual Studio 2017 project](./msvc/) or build Zydis using [CMake](https://cmake.org/download/) ([video guide](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fywLDK1OAtQ)).
#### Building Zydis - Using vcpkg
You can download and install Zydis using the [vcpkg](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) dependency manager:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg.git
cd vcpkg
./bootstrap-vcpkg.sh
./vcpkg integrate install
vcpkg install zydis
```
The Zydis port in vcpkg is kept up to date by Microsoft team members and community contributors. If the version is out of date, please [create an issue or pull request](https://github.com/Microsoft/vcpkg) on the vcpkg repository.
## Using Zydis in a CMake project
An example on how to use Zydis in your own CMake based project [can be found in this repo](https://github.com/zyantific/zydis-submodule-example).
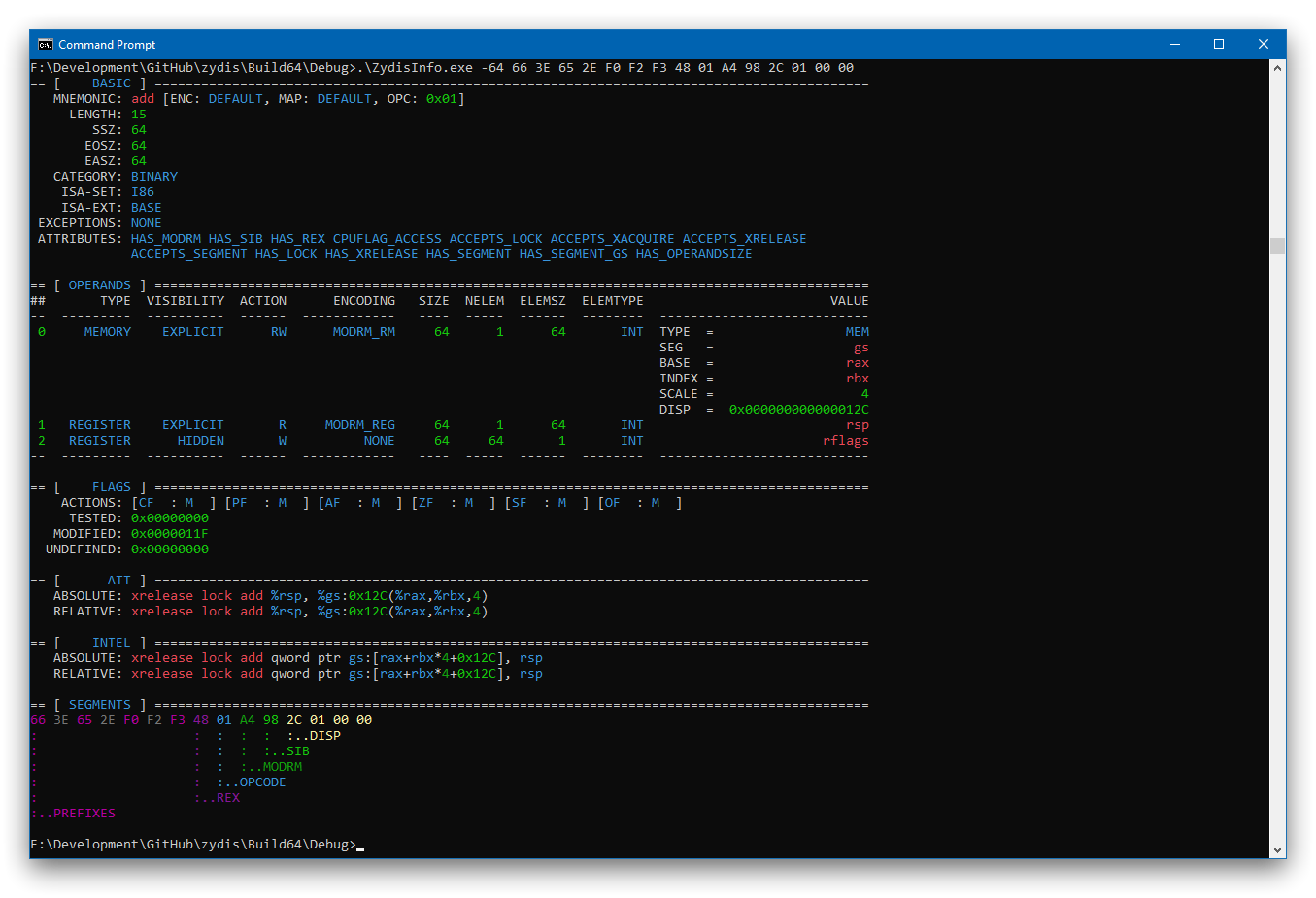
## `ZydisInfo` tool
## Bindings
Official bindings exist for a selection of languages:
- [Pascal](https://github.com/zyantific/zydis-pascal)
- [Python 3](https://github.com/zyantific/zydis-py)
- [Rust](https://github.com/zyantific/zydis-rs)
Unofficial but actively maintained bindings:
- [Go](https://github.com/jpap/go-zydis)
- [LuaJIT](https://github.com/Wiladams/lj2zydis)
- [Haskell](https://github.com/nerded1337/zydiskell)
## Versions
#### Scheme
Versions follow the [semantic versioning scheme](https://semver.org/). All stability guarantees apply to the API only — ABI stability between patches cannot be assumed unless explicitly mentioned in the release notes.
#### Branches & Tags
- `master` holds the bleeding edge code of the next, unreleased Zydis version. Elevated amounts of bugs and issues must be expected, API stability is not guaranteed outside of tagged commits.
- Stable and preview versions are annotated with git tags
- beta and other preview versions have `-beta`, `-rc`, etc. suffixes
- `maintenance/v2` contains the code of the latest legacy release of v2
- v2 is now deprecated, but will receive security fixes until 2021
## Credits
- Intel (for open-sourcing [XED](https://github.com/intelxed/xed), allowing for automatic comparision of our tables against theirs, improving both)
- [LLVM](https://llvm.org) (for providing pretty solid instruction data as well)
- Christian Ludloff (http://sandpile.org, insanely helpful)
- [LekoArts](https://www.lekoarts.de/) (for creating the project logo)
- Our [contributors on GitHub](https://github.com/zyantific/zydis/graphs/contributors)
## Troubleshooting
#### `-fPIC` for shared library builds
```
/usr/bin/ld: ./libfoo.a(foo.c.o): relocation R_X86_64_PC32 against symbol `bar' can not be used when making a shared object; recompile with -fPIC
```
Under some circumstances (e.g. when building Zydis as a static library using
CMake and then using Makefiles to manually link it into a shared library), CMake
might fail to detect that relocation information must be emitted. This can be forced
by passing `-DCMAKE_POSITION_INDEPENDENT_CODE=ON` to the CMake invocation.
## Donations
Since GitHub Sponsors currently doesn't support sponsoring teams directly, donations are collected and distributed using [flobernd](https://github.com/users/flobernd/sponsorship)s account.
## License
Zydis is licensed under the MIT license.

